
This will reduce the ability of the DNA to multiply and cause disease. For these reasons UV radiation is used as a method to sterilize surgical instruments because it kills the bacteria present and disrupts bacterial reproduction 2.
How-ever bacterial resistance to UV radiation varies.
Effect of uv light on bacterial growth experiment. The number of colonies surviving bacteria was counted under different UV light power and different exposure time. The experiment showed that there was no inhibition effect on the growth of bacteria using riboflavin alone. In UV alone group and UV-riboflavin group inhibition effect on the bacteria growth was found.
To Study the effect of UV exposure on the growth of bacterial cells. Mutations are a heritable change in the base sequence of DNA. Such mutations can be neutral or beneficial to an organism but most are actually harmful because the mutation will often result in.
Most bacteria are killed by the effects of UV light and UV light is therefore often used to sterilized surfaces. Also UV light damages the DNA of exposed microbes which can lead to cell death. UV radiation at 260nm is the most germicidal because this wavelength is the specific wavelength at which DNA maximally absorbs UV light.
The lack of an effect of UV light on reduction of mycobacteria in milk identified in our study was also observed by Donaghy et al. 2009 when using a pilot-scale UV light machine 30-W UVC output to treat milk inoculated with MAP. They concluded that the apparent resistance of MAP to UV light treatment could have been caused by the opacity of milk and the recalcitrance of MAP to inimical treatments.
EFFECTS OF UV IRRADIATION ON MICROORGANISMS I. OBJECTIVES To learn the effects of UV irradiation on different bacterial species. To learn if there is a correlation between the length of exposure to UV irradiation and the number of bacteria killed.
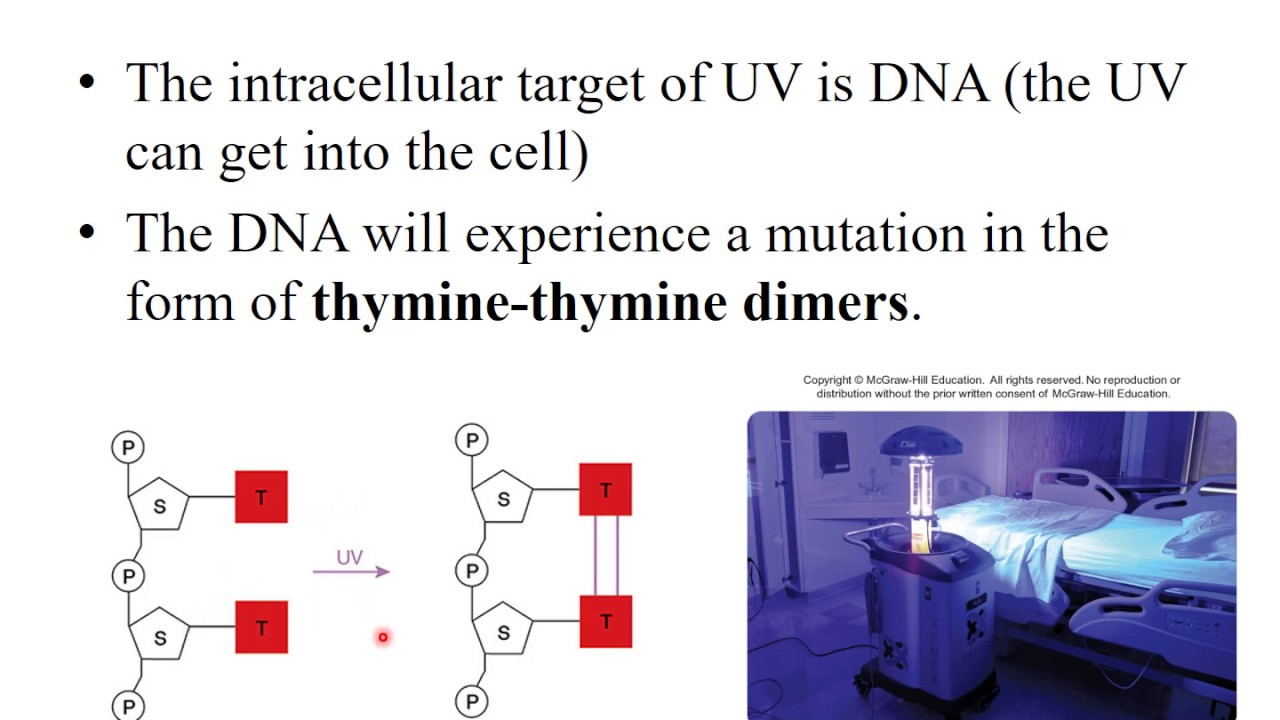
INTRODUCTION Light is a form of energy that travels in rhythmic waves. UV light affects growth by interfering with DNA resulting in thymine dimer formation. The dimerization is confined within adjacent thymine residues on same strand intrastrand.
These dimmer lesions have consequence on DNA functions including interference in DNA replication transcription etc so UV exposure of cells can lead to lethal effects for bacterial multiplications. Except the production of free radicals UV can directly affect DNA. The most common effect is at locations on the DNA molecule where two thymine T bases occur adjacent to each other.
UV irradiation causes the two T bases to covalently fuse together. Such structures are called thymine dimers and cause a distortion in the shape of DNA. What effect did UV radiation have on the bacterial growth.
When UV light is in operation of DNA viruses bacteria and other pathogens impacted. This will reduce the ability of the DNA to multiply and cause disease. Furthermore the UV light destroys harmful microbes such as bacteria yeast moulds viruses and algae.
Click to see full answer. Ultraviolet A light effectively reduces bacteria and viruses including coronavirus. Ali Rezaie Roles Conceptualization Data curation Formal analysis Funding acquisition Investigation Project administration Supervision Writing original draft Writing review editing.
List some factors that might have influenced the effect of UV light on each bacteria and explain the differences in results. Stearothermophilus was more affected by the UV light. Marcescens was expected to be more affected because it is non-endospore forming.
Bacteria DNA mutation science experiment sunlight ultraviolet radiation. Sunlight is essential for vital biological processes such as photosynthesis and vitamin D synthesis. However solar ultraviolet UV radiation can be detrimental to living beings.
It is associated with coral bleaching sunburn and melanoma. Ultraviolet UV radiation is known to inhibit cell growth and induce gene damage 1. For these reasons UV radiation is used as a method to sterilize surgical instruments because it kills the bacteria present and disrupts bacterial reproduction 2.
What about the bacteria growth rate after exposing to UV spectrometer for optical density measurement. Is that UV light effect the bacteria growth. Specifically when keep using the same culture.
Test different organisms for the effect of UV radiation. In this activity B. Cereus a resistant spore-forming Gram-positive bacterium was used to illustrate the severity of sunlights bactericidal effect.
How-ever bacterial resistance to UV radiation varies. For instance bacteria such as B. Subtilis that produce photoprotective pigment-covered.
Because UV light has the shortest wavelength thus having high energy thats why UV light is capable of killing pathogens even other viruses and bacteria. The wavelength of UV is from 200400 nm. This wavelength is effective in decontamination and sterilization because it cleaves the bonding molecular bonding which is in DNA OF MICROBES.
This video looks at the effect of UV light on microbial growth specifically comparing the effect of endospores versus vegetative cells. This is a video for. View Notes - 2-13 Ultraviolet Light Effects from BIO 2200 at Wayne State University.
The Lethal Effect of Ultraviolet Light on Microbial Growth pgs. Ultraviolet light C light wavelength 200 nm to 290 nm has been shown to kill cultures of antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. To evaluate the ability of ultraviolet light C to reduce the amount and type of bacteria present in chronically infected ulcers as well as to.
Ultraviolet light destroys harmful microbes such as bacteria yeast molds viruses and algae and ultraviolet radiation is less toxic to cave dwellers such as birds reptiles and visitors. So ultraviolet radiation can be a way to control microorganisms or reduce their numbers. This experiment examines the effectiveness of various antibiotics on bacterial growth the use of disinfectants and antiseptics to control bacterial populations and the lethal effect of ultraviolet light.
The microbial cultures tested included gram positive and gram negative bacteria bacterial spores and fungal spores. The microbes streaked on solid media were exposed to UV light. The inactivation of the order of four logs was observed for bacteria.
When the experiment was repeated bacteria mortality was approximately 40-75 for Serratia marcescens exposed to ultraviolet light at 254 nm for 15 seconds and about 75-90 bacteria mortality for the 30 second exposure. One minute of exposure time. The UV lights kill bacteria.
UV light in harmful to humans and all living things. UV radiation inhibited the growth of the E. Coli K-12 strain and possibly killed the bacteria.
The growth patterns reveal that the longer the period of UV exposure the greater the decrease in the number of CFUs. 3 UV laboratory lights of short wavelengths are capable of inhibiting bacterial growth.