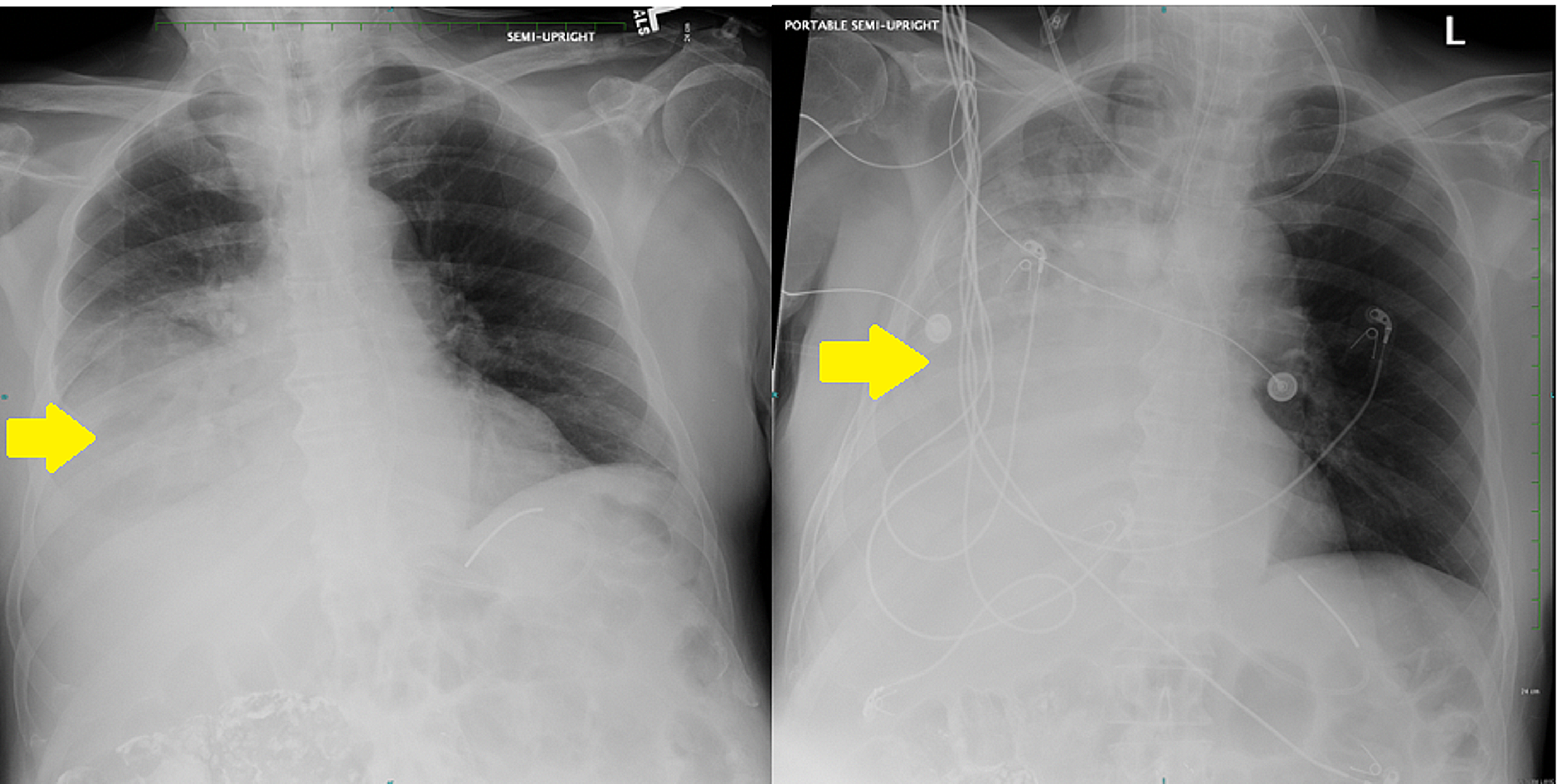
A The tip of the feeding tube white arrow is in the right lower lobe bronchus having descended in the trachea instead of the esophagus. After confirming correct tube placement removal of the stylet takes place.
Proper Dobhoff Placement PICO Question In Adult ICU patients will a two-step placement protocol improve RN small bore feeding tube insertion competence compared to LVHN standard practice policy.
Dobhoff feeding tube placement. Proper Dobhoff Placement PICO Question In Adult ICU patients will a two-step placement protocol improve RN small bore feeding tube insertion competence compared to LVHN standard practice policy. Blind Placement with radiographic confirmation Blind technique is defined as the clinician relying on manual feel. Tube placement zSlowly insert tube through nose zWhen resistance is met or patient gags have them start drinking water.
Then along with their swallowing slowly advance the tube. Continue this until you reach target distance. ZConfirm position with stethoscope over diaphragm while injecting syringe full of air through tube.
ZSecure tube to nose with tape. A Dobhoff tube is a type of feeding tube that is inserted into a patients nose threaded down the esophagus and into the stomach and down to the duodenum. A doctor or nurse must place this tube inside the patient as it is not always easy to get it in the correct location.
Feeding tube with guidewire brown tip that is 120cm preferred over blue tip dobhoff tube Lubricant 60 ml syringe. Steps for NG Feeding Tube Placement in an Awake Patient. Measure tube from tip of nose to subxyphoidprocess about 3035cm in most patients Step 2.
Place tube through nares and ask. Feeding via oro- or naso-gastric tube. A post pyloric Dobhoff tube is an excellent alternative although it can carry a serious risk of pneumothorax if placed blindly.
When a Cortrak machine is not available a two step technique using a chest x-ray to confirm placement in the esophagus and then through. How do you place a Dobhoff feeding tube. Radiographically a correctly positioned tube should pass vertically midline below the level of the carina it should not enter the right or left bronchi and the tip of the tube should be visible below the level of the diaphragm.
A Dobhoff tube was placed by a house physi-cian. The x-ray was read and placement confirmed. Tube feedings were initi-ated.
The patient experi-enced respiratory dis-tress. A review of the x-ray showed that the feeding tube was in the main bronchus. Confirmation that the feeding tube is properly placed in the stomach or small bowel involves.
Dobhoff tube is a special type of nasogastric tube NGT which is a small-bore and flexible so it is more comfortable for the patient than the usual NGT. The tube is inserted by the use of a guide wire called the stylet see image1 which removed after the tube correct placement is confirmed. The Dobhoff tube was introduced in the mid-1970s by.
Four Different Patients with Dobbhoff feeding Tubes. A The tip of the feeding tube white arrow is in the right lower lobe bronchus having descended in the trachea instead of the esophagus. B The tip of the Dobbhoff tube is in the descending limb of the duodenum yellow arrow considered the best position.
Thrombocytopenia TCP may be considered a contraindication to FT placement due to the potential risk of bleeding complications. Medical intensive care unit ICU adult oncology patients with attempted nasal or oral FT placement were evaluated in a 52-bed ICU at a comprehensive cancer center. End points were compared between patients with and without TCP platelet count.
Typically we use Dobhoffs only when were feeding TP. If it was supposed to be TP then a quick way to check placement is with a snap. You can put a 10cc syringe on the end of the tube and when you pull back on it the plunger should snap back down.
Of course this is not a 100 reliable method but it is a pretty good way to check until xray. A tube placed to one of three levels for delivery of nutritional feedings and medicine. The tube comes in one of three varieties a large weighted tip placed by the clinical service a small weighted tip placed by radiology and a more lucent end-hole tip placed by endoscopy.
A Dobhoff tube can be inserted at a patients bedside by a nurse or physician. The tube is inserted into the stomach by way of the nasal passage. A guide wire called a stylet is used during insertion.
The stylet is removed after the tubes correct placement has been confirmed. A Dobhoff tube has a weighted end that helps guide it through the digestive system. So-called enteral access systems can employ thin polyurethane feeding tubes with Dobhoff tips but use technology a video-scope tip for Covidiens product.
Electromagnetic sensors in a stylet for Corpaks to display feeding tube position to the user during placement. The original weighted polyurethane feeding tube designed for nasogastric and nasodueodenal feeding. Large bolus tip facilitates passage and helps maintain placement.
The feeding port is incompatible with luer lock or IV. Connectors reducing the risk of. Feeding to confirm placement.
Advance tube 25 cm remove stylet and put end of tube in. If bubbles are seen withdraw. If no bubbles.
Advance tube another 30-40 cm into stomach Nursing Interventions. Promote client comfort Assure client can move freely without tension on tube. To report our experience in treating hyperemesis gravidarum with nasogastric enteral feeding.
Seven women ages 17-36 years mean 27 years presented with intractable nausea vomiting dehydration and weight loss mean 13 lb and were hospitalized for management of symptoms and nutritional support. An 8-Fr Dobbhoff nasogastric feeding tube was placed and nutritional. Hereof how do you check the placement of a Dobhoff tube.
The feeding tube has a weighted metal tip and a guide wire for insertion. Tip of feeding tube should be in 2 nd or 3 rd portion of duodenum. Most however are placed in the stomach.
A Dobhoff naso-duodenal feeding tube DHT was inserted. On chest radiograph and a concurrent abdominal radiograph the DHT appeared to have been inserted into the left mainstem bronchus terminating in the left lower lobe Figure 1A and 1B. The nursing staff removed and replaced the DHT resulting in a similar radiograph.
A third placement was. Enteric access can be achieved by placement of feeding tubes in the stomach or past the pylorus into the small bowel. Dobbhoff feeding tubes are commonly used in surgical and trauma patients to achieve nasoenteral feeding.
Example of a Small-Bore Feeding tube. The current gold standard for diagnostic confirmation of a blindly inserted Dobhoff tube placement for purposes of enteral nutrition or medication delivery is radiographic examination level A evidence. Radiographically a correctly positioned tube should pass vertically midline below the level of the carina it should not enter the right or left bronchi and the tip of the tube should be visible below the level of the.
Without seeing the operative report I can say that I agree with the EGDDilation balloon of 43249. However the insertion of the g-tube should be coded as 43246. The Dobhoff tube is just the name of a naso-gatric tube.
49411 is for placement of interstitial device for. Dobhoff tube is flexible and thus more comfortable to the patient than other tubes. How Dobhoff tube is inserted.
A guidewire called the stylet is handy when inserting the tube. After confirming correct tube placement removal of the stylet takes place. It has a diameter of 4 mm which makes it comfortable for the patients.
What are the uses. Place the distal tip of the feeding tube at the patients lip or nares and use the tube to measure the distance back to one earlobe and then down to the tip of the xyphoid process. Place a mark at this point to indicate the tube position at the lip or nares that correlates with placement of the tubes distal tip in the stomach.