Factor III - tissue thromboplastin tissue factor Factor IV - ionized calcium Ca. First the development of recombinant activated factor VII rFVIIa has led to a much clearer understanding of the normal clotting cascade and to the possible role of this agent in treating the coagulopathy of liver disease.
If ever asked where a process occurs and you absolutely have no idea make an educated guess of the liver—Sarah Bellham.
Clotting factor not made in liver. The liver plays a central role in the clotting process and acute and chronic liver diseases are invariably associated with coagulation disorders due to multiple causes. Decreased synthesis of clotting and inhibitor factors decreased clearance of activated. Which clotting factor is absent.
Deficiencies of factor VIII and factor IX are known as hemophilia A and B respectively. Rare clotting factor deficiencies are bleeding disorders in which one or more of the other clotting factors ie. Factors I II V VVIIIVII X XI or XIII is missing or not.
Moreover which clotting factor is not produced in the liver. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside the liver throughout the body.
Coagulation abnormalities in liver disease. Hemostasis is intimately related to liver function because most coagulation factors are synthesized by liver parenchymal cells and the livers reticuloendothelial system serves an important role in the clearance of activation products. The extent of coagulation abnormalities depends upon the degree.
These include factors II V VII IX X XI and XII. All coagulation factors but VIII which is mainly produced by the endothelium are markedly reduced in patients with liver disease. This is due to synthetic liver failure and an inability to convert inactive precursors to functional coagulation factors.
Vitamin K deficiency is. People also ask what clotting factor is not made in the liver. Subsequently question is what are the 13 blood clotting factors.
The following are coagulation factors and their common names. Factor I - fibrinogen. Factor II - prothrombin.
Factor III - tissue thromboplastin tissue factor Factor IV - ionized calcium Ca. The clotting factors that are produced by the liver are I II V VII IX and X. The order in which the levels of these are reduced in liver disease is.
VII - the earliest to be reduced. II X - next to be reduced. I V - these persist despite severe liver disease.
Bleeding within the body activates a complex system of plasma proteins called coagulation factors which promote blood clot formation. The liver is responsible for producing most of these coagulation factors. Uncontrolled bleeding may occur if the clotting factors are not produced or if vitamin K is not absorbed.
Coagulation factors number and name. Plasma protein synthesized in liver. Precursor of fibrin converted to fibrin in final stage of clotting.
Serum is plasma minus fibrinogen. Plasma protein synthesized in liver. Synthesis requires vitamin K.
The liver makes clotting Factors I II VII IX and X. Fibrinogen is Factor I. Prothrombin is Factor II.
Factor IV is calcium which is not produced in the liver. If ever asked where a process occurs and you absolutely have no idea make an educated guess of the liver—Sarah Bellham. Causes of clotting problems include some liver diseases as many coagulation factors are made in the liver.
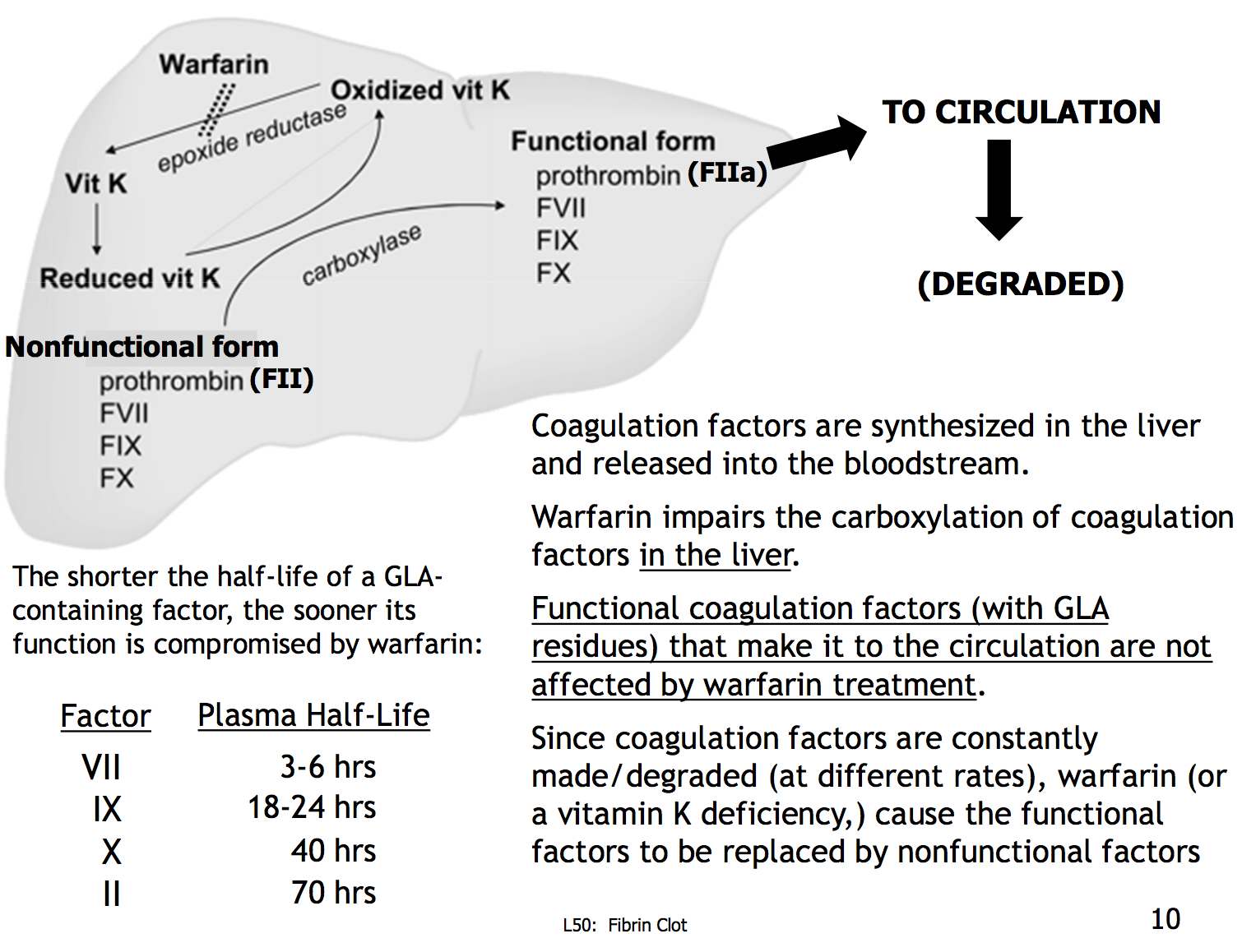
Not having enough vitamin K can also reduce coagulation factor levels as the vitamin is necessary for the creation of some clotting factors. When youre using coagulation tests to monitor liver failure the PT may be a better test than the PTT. The PT assesses factor VII which is the coagulation factor with the shortest half-life.
So the first test to become abnormal if you stop making coagulation factors is the PT. Then later as the other coagulation factors start to become noticeably less abundant the PTT becomes prolonged too. Liver failure is accompanied by multiple changes in the hemostatic system because of reduced plasma levels of procoagulative and anticoagulative clotting factors synthesised by hepatocytes and sinusoidal cells.
Vitamin K deficiency may coexist so that abnormal clotting factors are produced due to lack of gamma carboxylation. Activation of Vit K so it can make the K-dependent clotting factors. What coagulation factor is NOT made in the liver and has normal levels in the context of liver disease.
How does Liver Disease cause coagulopathies 4 mechanisms 1. Decreased synthesis of coagulation factors. What is the only clotting factor not made in the liver.
Factor VIII made by endothelial cells. Tissue factor which cleaves factor VII is also found in endothelial cells. Liver stops making.
The liver makes lots of proteins including clotting factors. Liver disease acute or chronic that knocks out enough active liver cells causes less protein to be made in general and clotting factors included. In addition platelets blood clotting cells decrease in liver.
Deficiencies of specific clotting factors cause coagulation disorders such as hemophilia excessive bleeding and thrombophilia excessive clot formation. The liver produces clotting factors I fibrinogen II prothrombin V proaccelerin VII cothromboplastin IX PLASMA thromboplastin and X Stuart-Prower factor. Factor VIII is an essential blood-clotting protein also known as anti-hemophilic factor.
In humans factor VIII is encoded by the F8 gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside the liver throughout the body.
This protein circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form bound to another molecule called von Willebrand factor. Nine of the ten proteins called coagulation factors because they are biologically active in blood coagulation are produced by the parenchymal liver cell 13 16. The exception is factor viii the bulk of which is synthesized elsewhere probably in the cells of the reticuloendothelial system.
The biosynthesis of four of the nine factors produced by the liver-cell is vitamin K dependent. These are factors ii vii ix and x the factors. Vitamin K deficiency may coexist resulting in defective carboxylation of clotting factors and inhibitors.
During liver failure there is a reduced capacity to clear activated haemostatic proteins. An important function of the liver is the synthesis and secretion of blood coagulation factors. Within the liver hepatocytes are involved in the synthesis of most blood coagulation factors such as fibrinogen prothrombin factor V VII IX X XI XII as well as protein C and S and antithrombin whereas liver sinusoidal endothelial cells produce factor VIII and von Willebrand factor.
First the development of recombinant activated factor VII rFVIIa has led to a much clearer understanding of the normal clotting cascade and to the possible role of this agent in treating the coagulopathy of liver disease. 1-3 Moreover two important studies have raised serious questions about the clinical use the prothrombin time PT and.