Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Stack the subshells in order of energy with the lowest-energy.
A n 3 l 2.
Atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. If you are still not getting the Nitrogen Electron Configuration of the element nitrogen then the full electronic configuration of nitrogen is written as the following. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. If we gave you brief information then the first two electrons lie in the 1s orbital following the next 2.
Atomic nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and 4 valence orbitals 2s 2p x 2p y and 2p z. Also what is the configuration of nitrogen. He 2s2 2p3.
Secondly what is the orbital diagram for phosphorus. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. Well put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in.
Normally nitrogen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. And in Hunds principle the electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p x1 2p y1 2p z1. The electron configuration of nitrogen in excited state is N 7 1s 2 2s 2 2p x1 2p y1 2p z1.
The last orbital of nitrogen is p. Draw the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. The simplified pictorial notation of the arrangement of the electrons within the different energy levels or orbitals of an.
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital.
The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N nitrogen. Stack the subshells in order of energy with the lowest-energy.
Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. How many electrons does a fe atom have in its 3. For example boron is in the 2p block of the periodic table and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it.
Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital energy level diagram of nitrogenoxygen duration. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals.
Here is a schematic orbital diagram for a hydrogen atom in its ground state. These are also known as electron in a box diagrams. Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen.
For example boron is in the 2p block of the periodic table and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it. Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.
Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma. Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen.
Start by adding the appropriate subshells. For example boron is in the 2p block of the periodic table and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it. Next click the orbitals to add electrons represented as arrows.
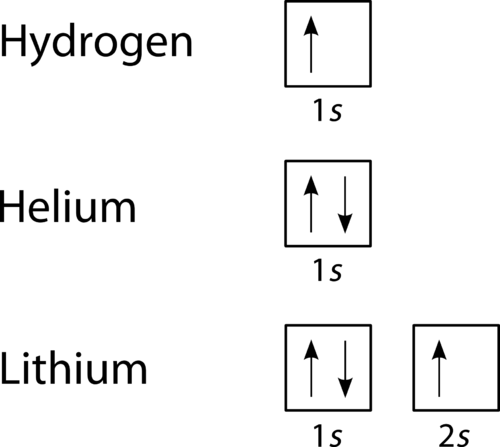
For boron you would need to show a total of five electrons. Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams. Orbital diagram of Hydrogen H 2.
Orbital diagram of Helium He 3. Orbital diagram of Lithium Li 4. Orbital diagram of Beryllium Be 5.
Orbital diagram of Boron B 6. Orbital diagram of Carbon C 7. Orbital diagram of Nitrogen N 8.
Orbital diagram of Oxygen O 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine F 10. The periodic table shows us that nitrogen N has an atomic number of 7.
As a result a neutral nitrogen atom will have 7 electrons. In orbital filling diagrams s-sublevels have 1 orbital and p. Solved create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen st answer to create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen start by adding the appropriate subshells for example boron is in the create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen in some cases we may need to slightly alter the design color or even accessories we want a new thought for it then one of them is this create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen create.
Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom. Diagram of Hunds rule in boron carbon nitrogen and oxygen. Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations.
In the same way the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will beGiven the same amount of absorbed. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. The orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen is a a b b c c d d the electron configuration.
It depends on the atom. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2. The choice A accurately specifies and illustrates the orbital diagram of a Nitrogen atom with 7 electrons.
Based on the number of electrons in a Nitrogen atom there are two energy levels the s and p sub-levels. Nitrogen 2 5. The first energy level S will take up two electrons with opposite spin.
Use the orbital diagram for nitrogen to write quantum numbers for the 3rd electron of the n atom. N defines the energy level. N defines the energy level.
The diagram shows the number of subshell by using boxes or lines for electrons use three for p orbitals five for d orbitals and 7 for f orbitals. Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. 93 50 ratings Problem Details.
Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Learn this topic by watching The Electron Configuration Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems The Electron Configuration Practice Problems.
Nitrogen is neutral and its atomic number is 7 hence the number of protons and electrons available for its Bohr diagram is also 7. The number of neutrons for the Bohr diagram of Nitrogen can be founded by subtracting the number of protons from the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals.
Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two perpendicular pi bonds. Three filled bonding orbitals.
And three empty antibonding orbitals. Orbital Diagram Of Nitrogen. Molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory molecular orbital theory home faculty molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms that is in.
A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining Two atomic orbitals in phase create a larger electron density which leads to the σ orbital. If the two 1s orbitals are not in The MO diagram correlates with the experimental photoelectron spectrum for nitrogen. Use the orbital diagram for nitrogen to write quantum numbers for the 3rd electron of the n atom.
The fact is that it takes less energy for an electron to be placed in the 4s sublevel than in the 3d. In its ground state an atom of an element has two electrons in all orbitals related to the atoms highest energy level for which n6. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons.
A n 3 l 2. Quantum Numbers Atomic Orbitals And Electron Configurations 4 quantum numbers electron configuration. Use the orbital diagram for nitrogen to write quantum numbers for the 3rd electron of the n atom.
The magnetic quantum number mℓ the spin quantum number ms the principal.